Answer Sexual reproduction is a process which involves production of seeds It requires two parents Most plants reproduce sexually with the help of flowers The main function of a flower is to reproduce and therefore develop new seeds that can grow into new plantsWhat are some examples of asexual plants?Nov 03, 13 · Produce pollens "Yellow powder" Produce "make" the seeds when the pollens are carried by the wind and land on the female cone 9 THE FLOWER The flower is the part of the plant which is responsible for reproduction

There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express
How does a seed reproduce
How does a seed reproduce-For example, kauri seed must be sown immediately once it has ripened Some plants don't produce seeds, such as most varieties of banana New plants may take a long time to reach maturity (adulthood) when grown from seed, for example, rhododendron The variation in the plants produced by seed might make it difficult to grow a uniform crop to sellCan dormant seeds be stored longer than nondormant ones?



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science
This video is made for the students to learn easily the examples of types of seeds ie albuminous and non albuminous seedsPlease do like share and subscribeReproductive Phase Grasses may reproduce sexually by seed (sexual reproduction), or asexually via vegetative propogation (tillers which arise from adventitious buds on culm nodes, rhizomes, and stolons) This section deals only with sexual reproduction involving flowers, pollination, and seedsMay 16, 17 · They are an important development in higher plants in order to make the reproduction successful Angiosperms' seed contains three constituents a seed coat, an embryo, and an endosperm The embryo sac of angiosperms undergoes double fertilization, simultaneously developing an embryo and an endosperm
Jul 03, 19 · Many sporozoans can alternate between sexual and asexual reproduction in their life cycles Toxoplasma gondii is an examples of a sporozoan that infects mammals, particularly cats, and can be transmitted to humans by animals T gondii causes the disease toxoplasmosis which can result in brain diseases and miscarriages in pregnant women Toxoplasmosis is commonlyNov 08, 19 · Vegetative propagation or vegetative reproduction is the growth and development of a plant by asexual means This development occurs through the fragmentation and regeneration of specialized vegetative plant parts Many plants that reproduce asexually are also capable of sexual propagation(2) the megasporangium, unlike that of heterosporous seedless plants, is covered by one or two cellular layers called integuments and is termed an ovule;
A number of parts of the reproductive process are common to both angiosperms and gymnosperms (1) they produce seeds at maturity;Apr 25, 13 · Seed food reserves are stored outside the embryo, and the cotyledons serve as conduits to transmit the brokendown food reserves to the developing embryo The seed consists of a toughened layer of integuments forming the coat, the endosperm with food reserves and, at the center, the wellprotected embryoBut Sometimes no, for a seedlot that contains rotting pieces of fruit will probably go mouldy and the seeds die (See B 30–34 for more information on seed handling)




Reproduction In Human And Plants Male Reproductive System



Saving Seed Will The Seed Produce Plants Similar To The Plant It Was Collected From
With seeds, all plants, considered spermatophytes, are spread and propagated Inside the seed, there is the embryo from which the new plant will come out if all the right conditions are met The function of seeds is to achieve plant germination and make sure it comes out correctlyGive two examples All plants can reproduce through seeds, except for those hybrids/cultivars that are so radically modified that they have lost reproductive function Seedless watermelon and hybrid tea roses would be examples of those that CANNOT reproduce form seed 490 viewsThe phenomenon of Seed Dispersal helps in reproduction in plants But what ex



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs



2
Seed 1 Part of the sexual reproduction of angiosperms (flowering plants) and gymnosperms (cone plants) Contains an embryo and its food store, which creates a new plant when conditions are right 2 Offspring or progeny spores Small reproductive structures that can grow into a new individualSeeds generated by apomixis are a means of asexual reproduction, involving the formation and dispersal of seeds that do not originate from the fertilization of the embryos Hawkweed (Hieracium), dandelion (Taraxacum), some Citrus (Citrus) and Kentucky blue grass (Poa pratensis) all use this form of asexual reproductionGymnosperms are any type of vascular plant that reproduce via an exposed seed While most flowering plants, known as angiosperms, have a seed enclosed in an ovary or fruit, gymnosperms (which means "naked seeds") do not have covers on their seeds Some examples of nonflowering plants that are classified as gymnosperms include




Angiosperm Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Seed Dispersal Wikipedia
Feb 16, 15 · The pollen tube deposites the sperm cells in the archegonium and fertilization occurs The embryo develops in the ovulate cone and a seed is formed from the mature ovule Seeds contain nutrients that will feed the embryo as it grows and a protective coat Seeds contain the diplod embryo and will grow into the mature sporophyte Examples of MaleMar 13, 18 · The purpose is to make new plants Plants want to spread their seeds to increase reproductive success To do this, plants use seed dispersal, or methods to spread their seeds in a large geographicThe seeds of the orchid plant, dandelions, swan plants, cottonwood tree, hornbeam, ash, cattail, puya, willow herb, are all examples of plants whose seed are dispersed by the wind Seed Dispersal by Water In this method of seed dispersal, seeds float away from their parent plant




Vegetative Reproduction In Plants Advanced Ck 12 Foundation



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce
Seeds which have wings and hairy parachutes on them are carried by the wind Eg – sycamore, ash, maple, lime, dandelion and thistle When pods dry, they split open suddenly and shooting the seeds away from the parent plant and this is easy when the wind is there Eg – peas, lupins, laburnum and gorseEver wondered how seeds from one Plant get sown in a different area altogether?Jan 17, · The parent plant produces seeds without fertilization Fragmentation is another form of asexual reproduction It involves new plants growing from small parts of the parent plant that fall to the ground For example, animals or the wind can break stems or leaves off plants




Science Plant Reproduction Seed And Germination Hindi Youtube




Seeds And Fruits Concepts Development Of A Fruit And Solved Example
Sexual reproduction results in offspring genetically different from the parents Asexual offspring are genetically identical except for mutation In higher plants, offspring are packaged in a protective seed, which can be long lived and can disperse the offspring some distance from the parentsReproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life;Plants are obtained from seeds



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science
Other articles where Seed propagation is discussed propagation Sexual propagation With crops that produce seed freely and come true closely enough for the purposes in view, growing from seed usually is the cheapest and most satisfactory method of plant propagation Many types of seeds may be sown in open ground and, barring extremeFor example, runners develop from a strawberry plant's crown As the runner branches laterally, it slowly descends to the soil As a result, it grows a new root and foliage system, referred to asJul 01, 21 · For example, tomato seeds have a minimum germination of 50°F, a maximum of 95°F, and an optimum germination temperature of 80°F When germination temperatures are listed, they are usually optimum temperatures For most plants, 65 to 75°F is best




Plant Reproduction Ck 12 Foundation




Asexual Plant Reproduction May Seed New Approach For Agriculture Hhmi
Dec 06, 19 · Ans The postfertilisation events in angiosperms include (i)Endosperm and embryo development (ii)Maturation of ovule into seed (iii)Maturation of ovary into fruit 6Some angiosperm seeds are said to be 'albuminous', whereas few others are said to have a perisperm, Explain each with the help of an exampleMar 30, · By Staff Writer Last Updated March 30, Some examples of vegetative propagation are farmers creating repeated crops of apples, corn, mangoes or avocados through asexual plant reproduction rather than planting seeds Vegetative propagation can be accomplished from sideshoots, slips, stems and sections of tubers, bulbs or rhizomesReproduction by seed Usually perennial weeds first infest an area byseed Reproduction by seed is called sexualreproduction It requires the fertilization of anegg by sperm, usually in the form of pollenPollination of the egg in a flower results in seedthat is capable of producing a new plant




Seed Plants Angiosperms Concepts Of Biology



Flowers Sunset Magazine
Particularly favorable does reproduction from seed con tribute significantly to maintenance and spread of the species (Andrejak and Barnes 1969, Maini 1974) Therefore, Baker's (1918b) suggestion that sexual reproduction is defective because of failure of seed set or low germinability of seeds was widely accepted forEach individual organism exists as the result of reproductionThere are two forms of reproduction asexual and sexual In asexual reproductionSometimes yes for example a seedlot with hard seed coats will usually keep best if they have not yet been pretreated;




Plant Reproduce




What Are The Different Ways Of Reproduction In Plants Give Examples Different How Or Rmjnaiion Take Place T Stud Evs Our Resources Meritnation Com
(3) there is a minute passageway, or micropyle, through the integuments;Mar 10, · Rhizomes grow indefinitely, so they can cover a wide surface Lots of types of grass, reeds and trees like populus and oaks are examples of rhizomes Plant reproduction without seeds is present in mosses and ferns These plants combine sexual and asexual reproduction When the female and male gamete meet, structures are formed called spores(4) the ovule matures as a seed
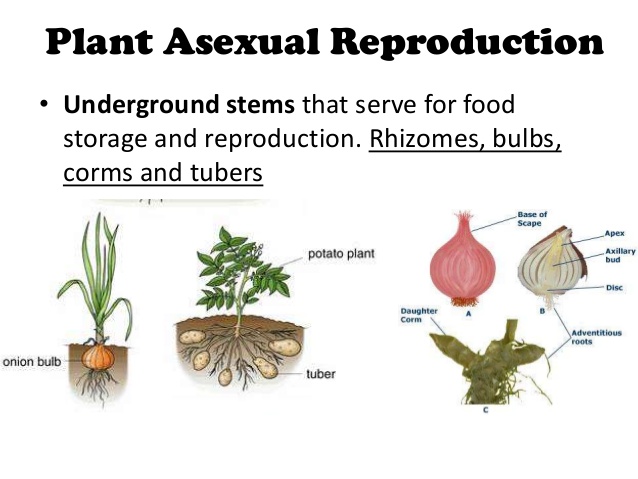



Advantages And Disadvantages Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants Science Online




Seed Wikipedia
The number of offspring or seeds produced at each reproductive cycle by a plant is called clutch size For example, a plant produces 1000 seeds in its one season It is its clutch size Generally plants which large clutch size (produce large number of seeds) produce small seeds or fruits(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of wind, water and animal Question 2 Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction Give examples Answer 2 The different methods of asexual reproduction Vegetative propagation It is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and budsExample Mango Advantages of Vegetative Propagation It allows quick and easy propagation Plants can bear flowers, fruits earlier than those produced from seeds It is only the possible method of reproduction of such plants which have lost the capacity to produce viable seeds The offspring is an exact copy of the parent Solved Questions For




Pin On Xaiden
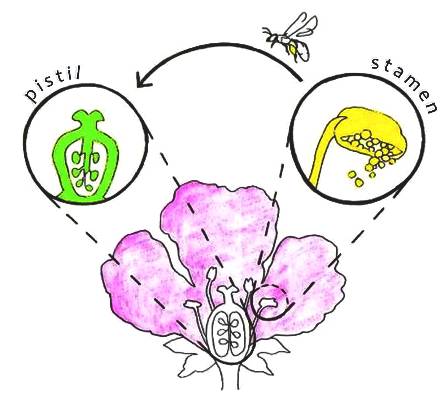



Flower Anatomy
The seed contains the embryo covered by the seed coat Cotyledon present in the seed helps in the nourishment of the developing baby plant on germination of the seed Learn more about Vegetative Propagation here Questions For You Q1 Which of the following statements is/are true for sexual reproduction in plants?The lush palms on tropical shorelines do not depend upon water for the dispersal of their pollen, fertilization, or the survival of the zygote, unlike mosses, liverworts, and ferns of the terrain Seed plants, such as palms, have broken free from the need to rely on water for their reproductive needsMar 01, 16 · This is an example of sexual reproduction However, this is not the only way to propagate a plant Other ways do not involve seeds and utilize asexual reproduction instead
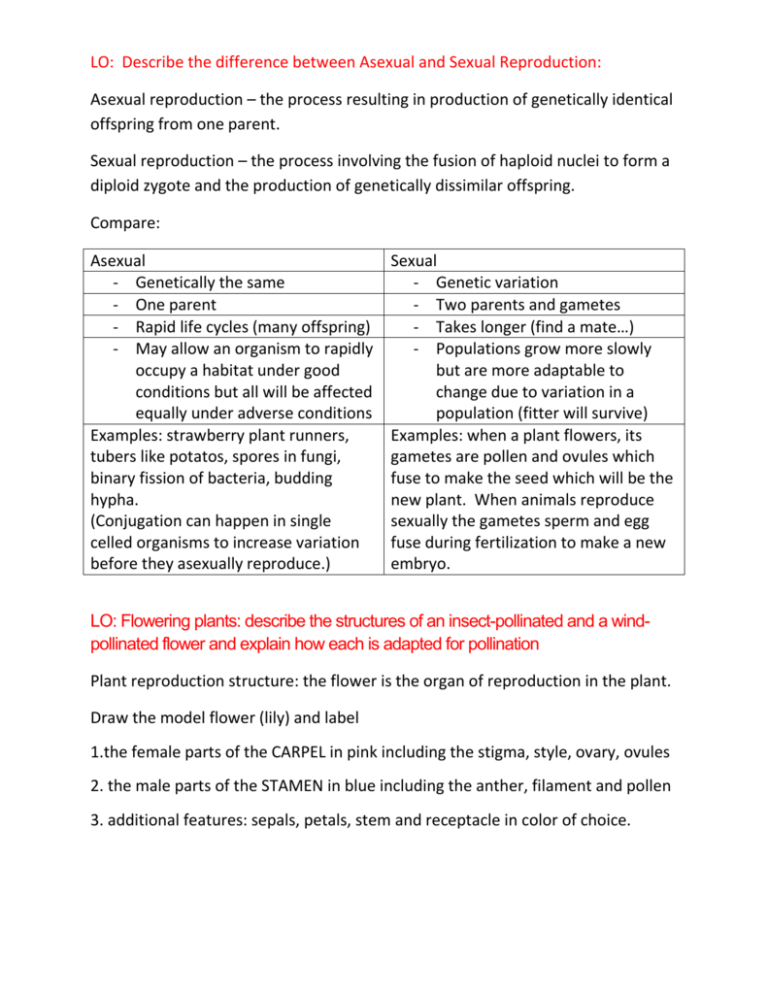



Lo Describe The Difference Between Asexual And Sexual



Tomatosphere Tomatosphere The Life Cycle Of A Tomato Plant
An totally asexual plant is a sterile hybrid which cannot produce viable seeds, but which propagates asexually by runners (strawberries), cuttings, bulb division, tubers, or grafting Many fruit trees areApr 03, 11 · Seed Formation If all the endosperm is absorbed by the developing embryo the seed is a non endospermic seed eg broad bean 43 Seed Formation If all the endosperm is not absorbed by the developing embryo the seed is an endospermic seed eg MaizeExamples of seed dispersal by wind;




Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub
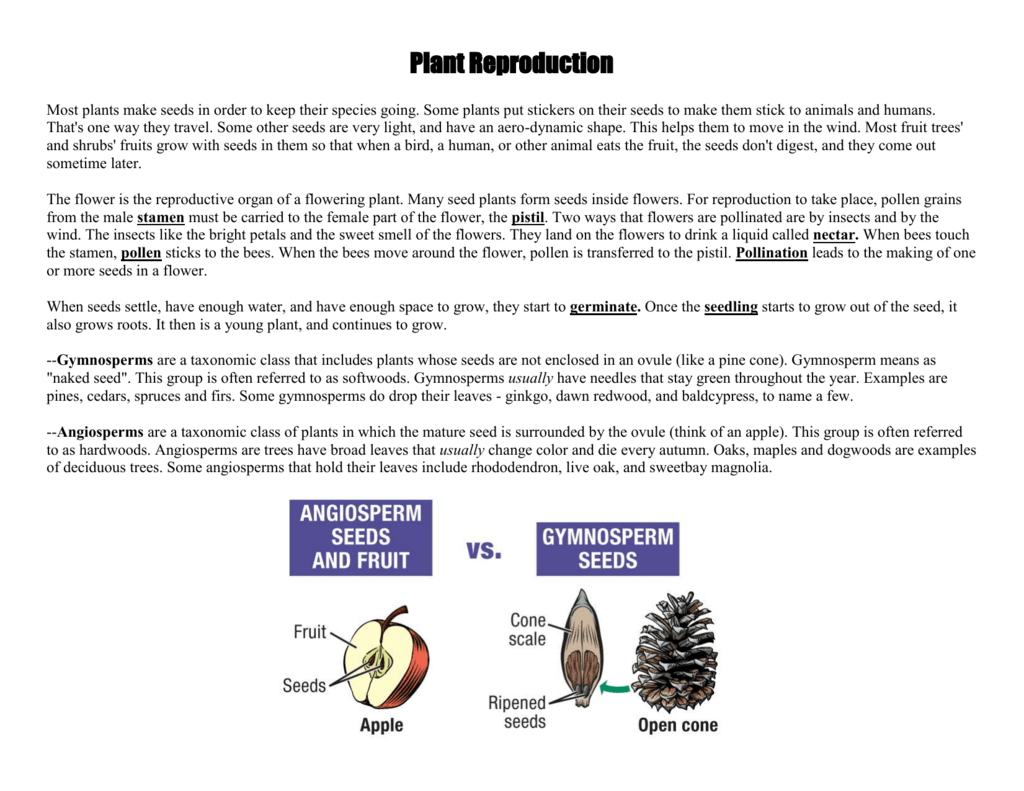



Plant Reproduction
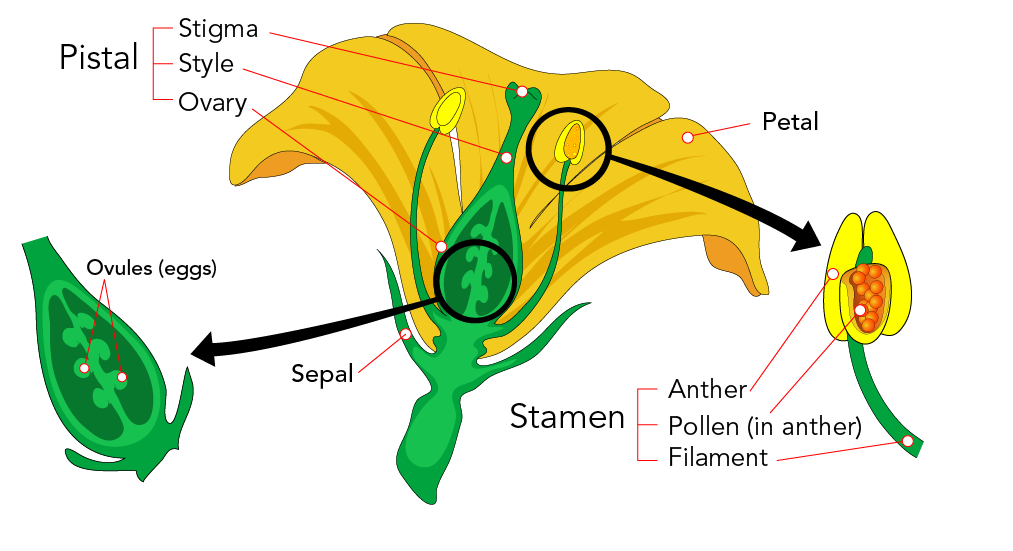
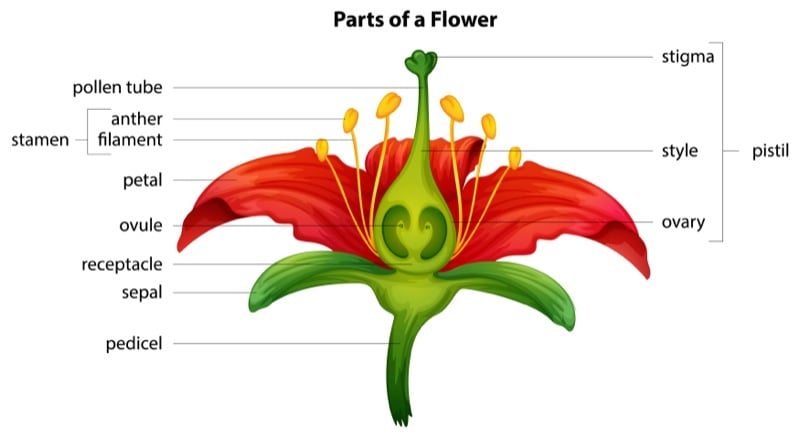
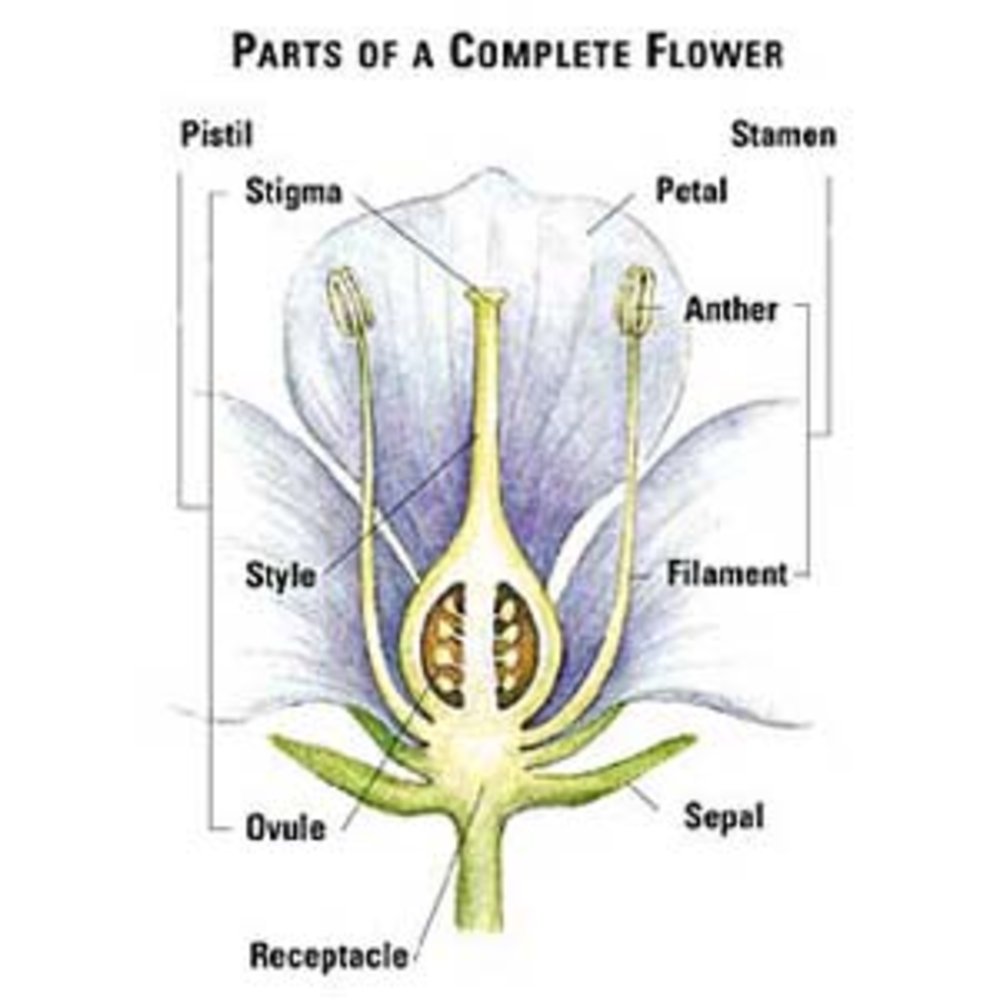
Sexual reproduction in plants takes place in flowers The complete flower typically consists of four parts Petals Sepals Stamen (male reproductive part) Pistil/Carpel (female reproductive part) Stamen (male reproductive part) consists of anther and filament The anther is a saclike structure that produces and stores pollen
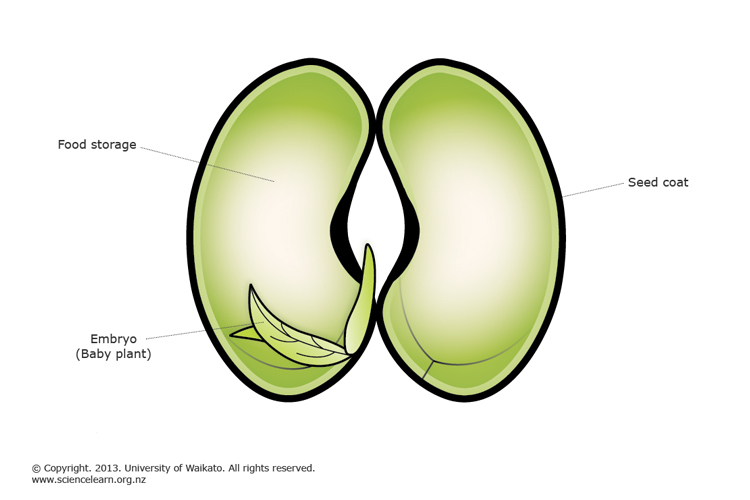



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub
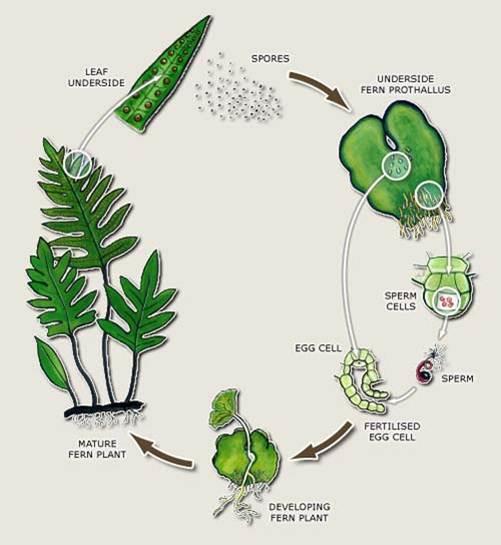



Seeds Vs Seedless Plants Biology Socratic




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica
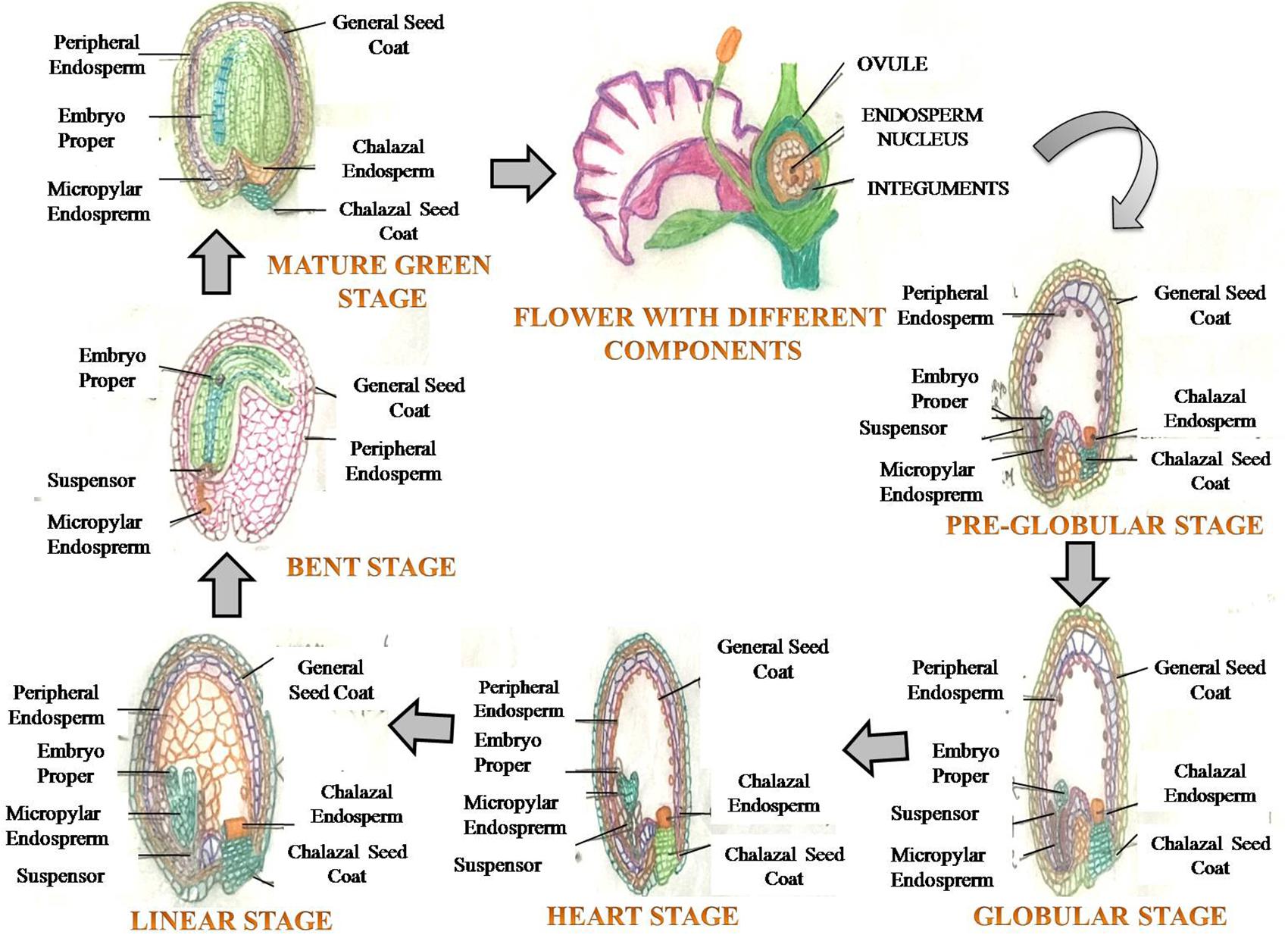



Frontiers Drought Or And Heat Stress Effects On Seed Filling In Food Crops Impacts On Functional Biochemistry Seed Yields And Nutritional Quality Plant Science



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C




Flowering Plant Reproduction Development And Chegg Com




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii




Vegetative Propagation In Plants Definition Methods Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
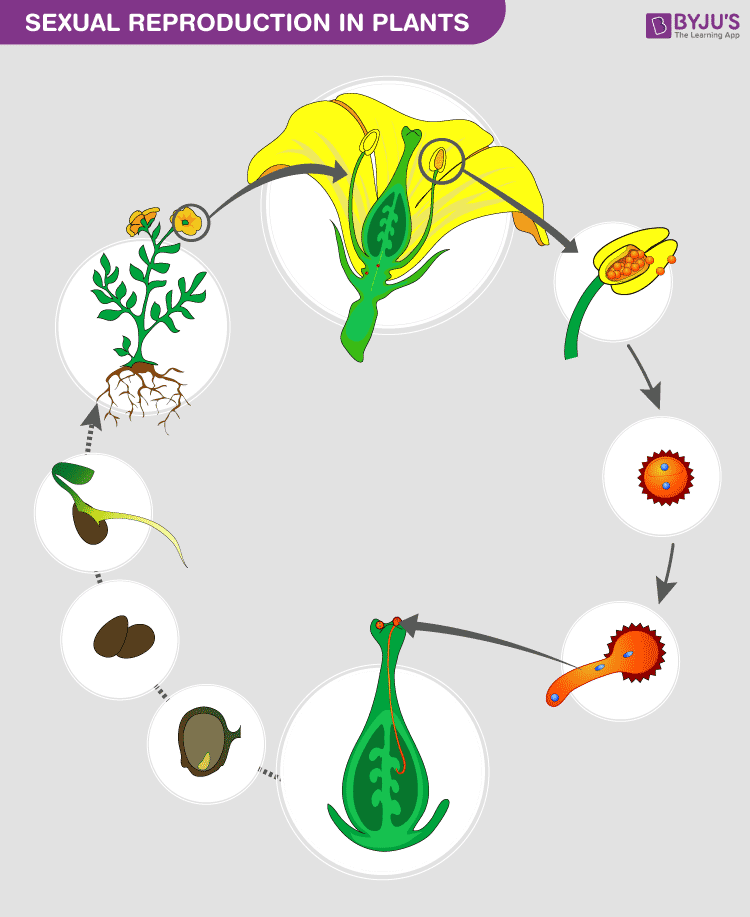



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Features And Its Process




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii




Ovary Botany Definition Structure Britannica
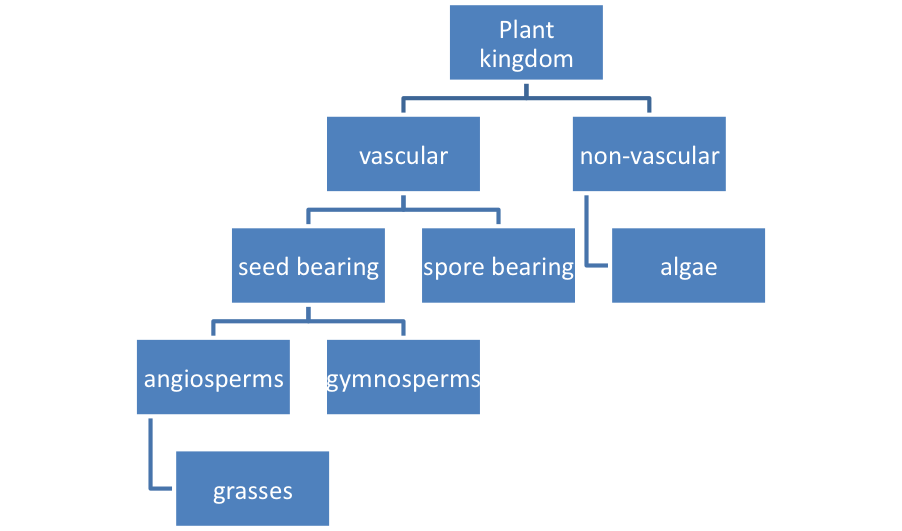



Lesson 4 Plant Classification Mpalalive
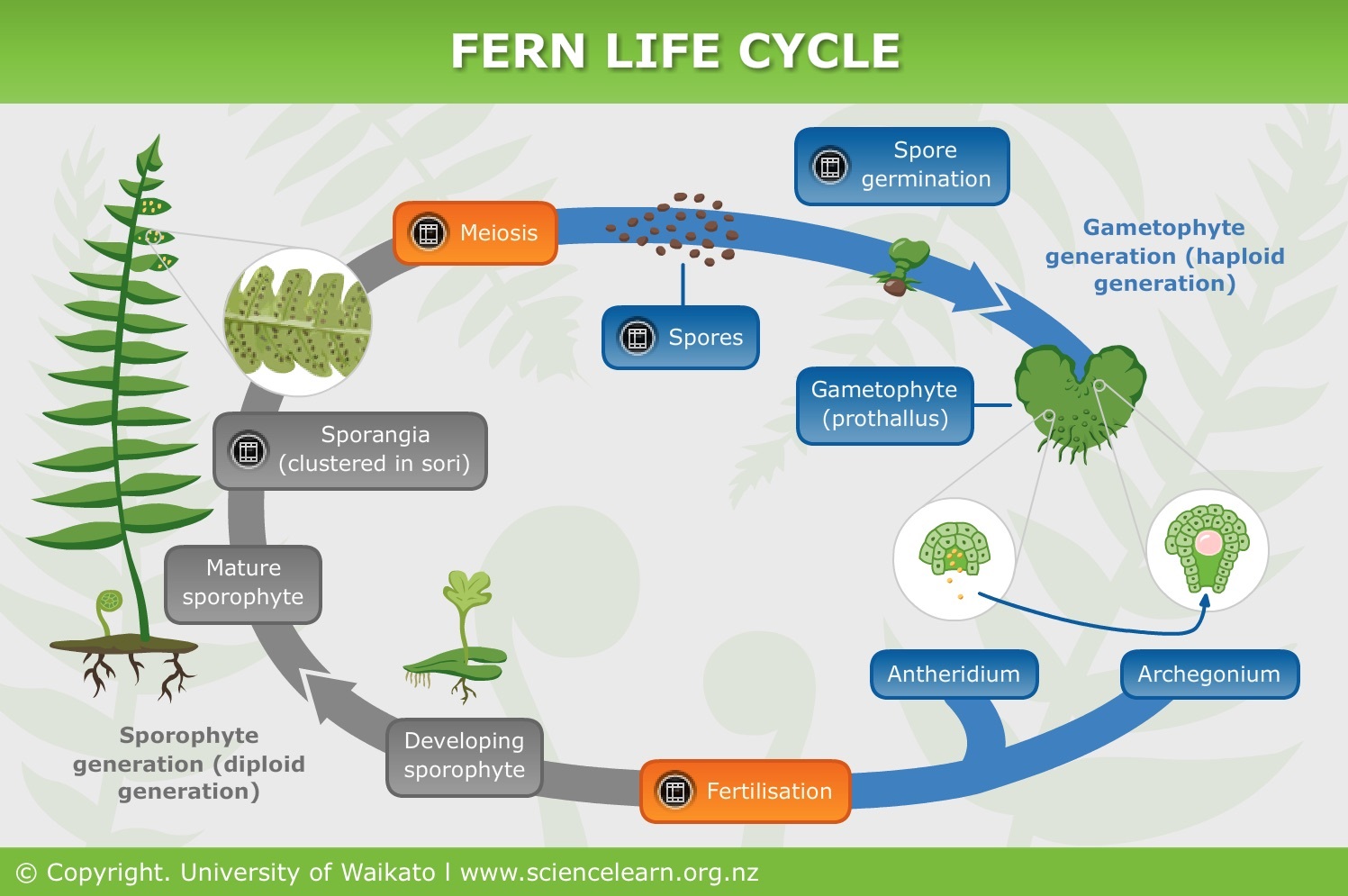



Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub




What Are The Stages Of A Plant S Life Cycle c Bitesize




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub
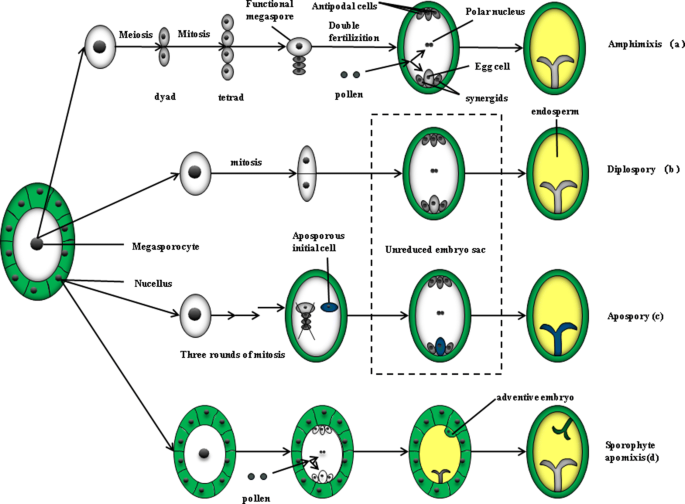



The Steps From Sexual Reproduction To Apomixis Springerlink




Pollination And Seed Dispersal Science Video For Kids Grades K 2
/cycad_cones-5ae333e9a9d4f9003736fc5e.jpg)



Gymnosperms Definition Examples And Reproduction




Sexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii




Examples Of Possible Log Log Relationships Between Direct And Accessory Download Scientific Diagram




Gymnosperms Naked Seed Plants An Overview Of Biodiversity




Seed Dispersal Methods Benefits Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Pin On Art Of Gardening




Plant Reproductive System Definition Types Examples Facts Britannica




Asexual Reproduction Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary



Plants 1 Plant Parents Science Netlinks



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Learn Biology Class 7 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network




Reproductive Systems And Evolution In Vascular Plants Pnas




Biology Reproduction Notes



Reproduction In Plants Psle Science




Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S




Reproductive Plant Parts Osu Extension Service




Sexual Reproduction Of The Flowering Plant Learning Objectives 1 4 State The Structure Function Of The Floral Parts Including Sepal Petal Stamen Carpel Ppt Download




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Types Of Reproduction In Plants Youtube



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications
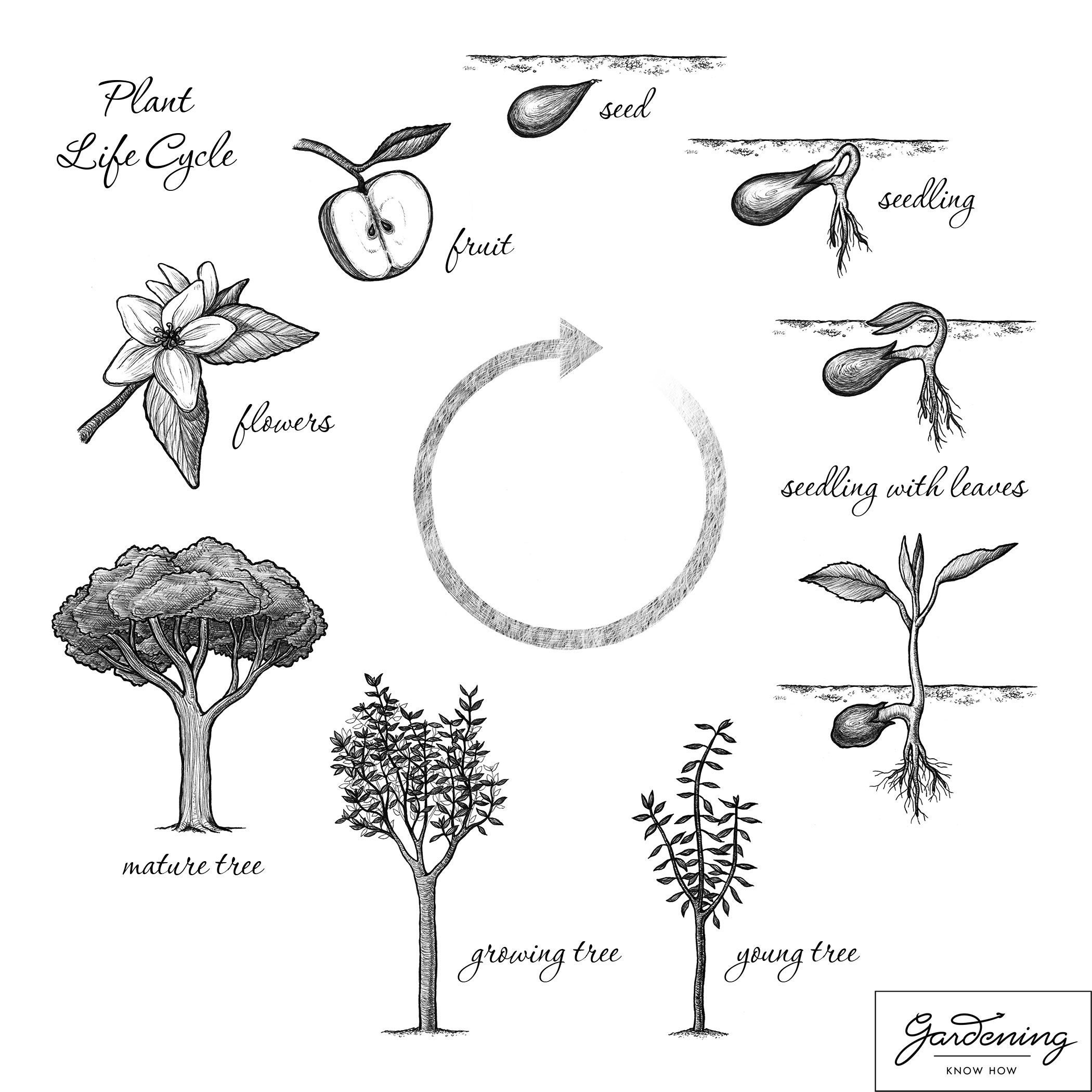



Basic Plant Life Cycle And The Life Cycle Of A Flowering Plant Gardening Know How
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gymnosperm_reproduction-5ae33a4e0e23d90039a3dba5.jpg)



Gymnosperms Definition Examples And Reproduction



1



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs



1



How Do Trees Reproduce Quora
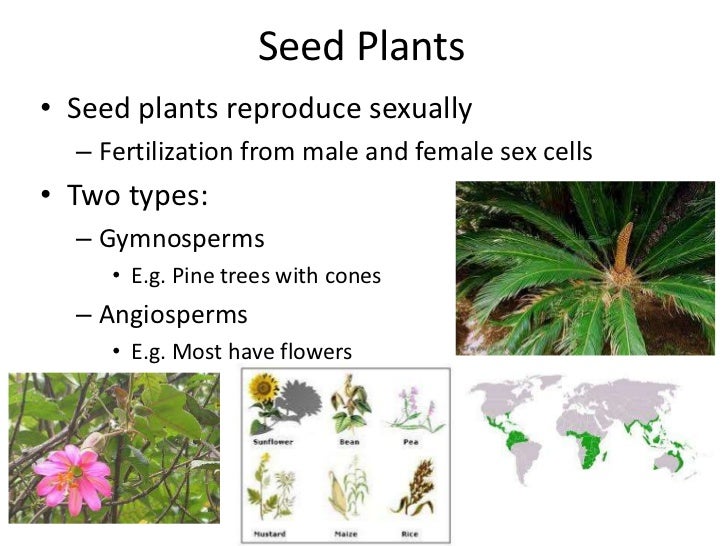



Plant Reproduction Seed Plants




Science Plant Reproduction Without Seed English Youtube
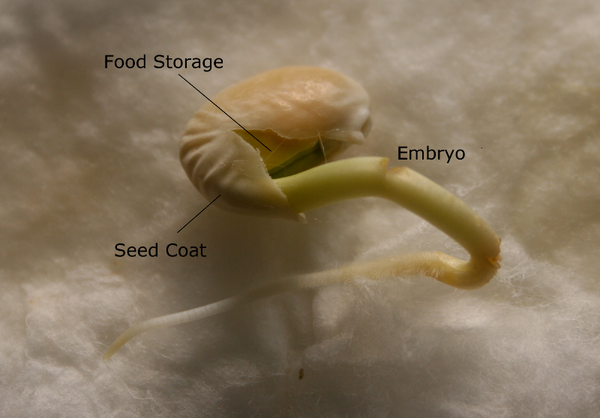




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications



Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Plants




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express
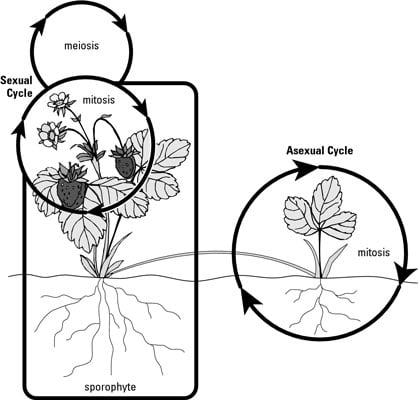



Plant Reproduction Dummies




Understanding Students Conceptions Of Plant Reproduction To Better Teach Plant Biology In Schools Lampert 19 Plants People Planet Wiley Online Library
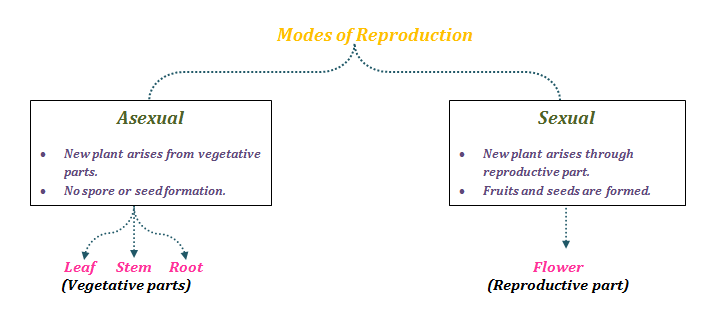



Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S



1




Plant Asexual Reproduction Educational Video For Kids Youtube



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C




Plant Reproduction Bioninja
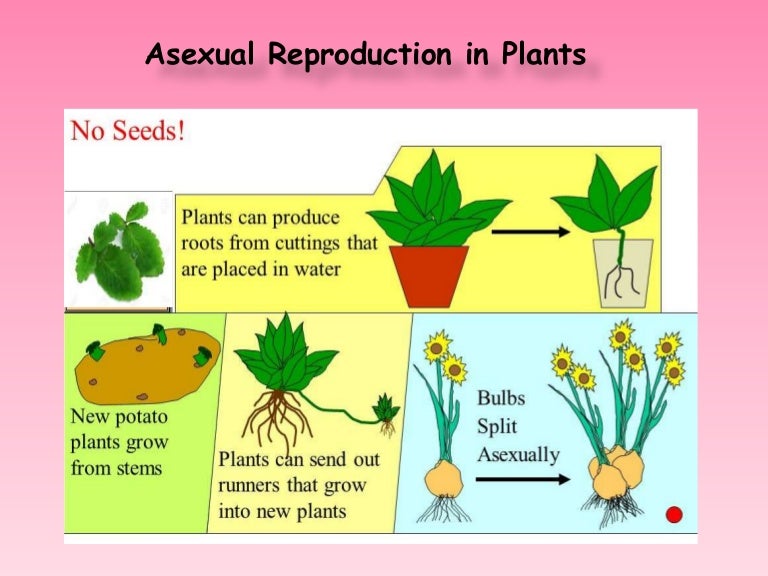



Asexual Reproduction In Plants




Biology Reproduction Notes




Fruits Flowers And Seeds Biology Online Tutorial



Ginseng Reproduction



Asexual Reproduction Biology Ii




Plant Reproductive System Angiosperms Britannica




Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download




Flowering Plants Life Cycle Examples Study Com




Plant Reproduction Bioninja
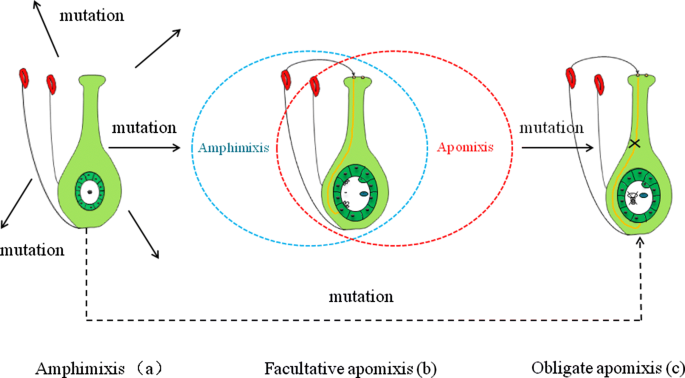



The Steps From Sexual Reproduction To Apomixis Springerlink
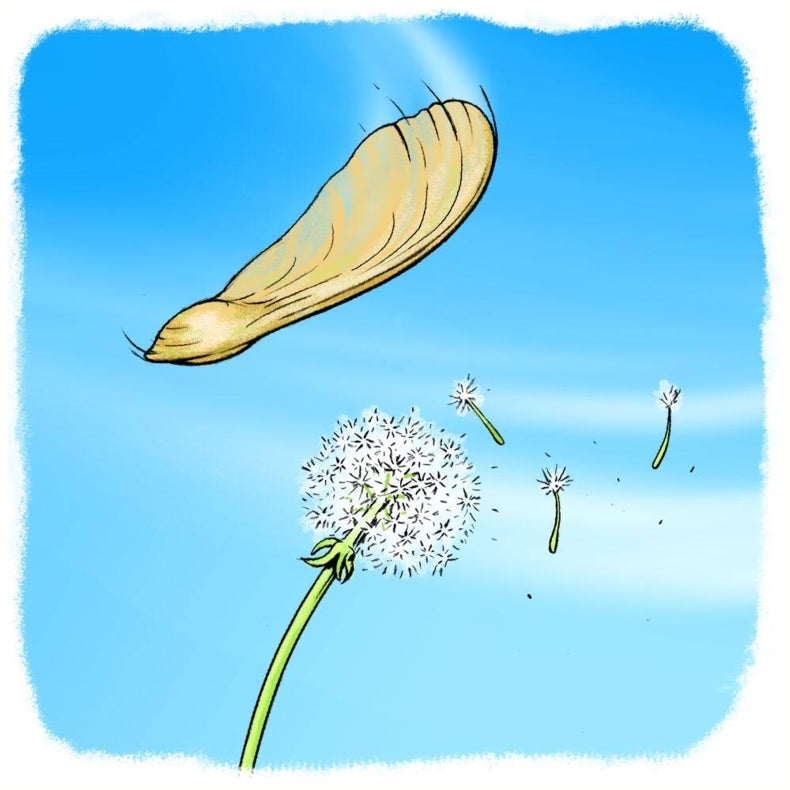




Gone With The Wind Plant Seed Dispersal Scientific American




Chapter 22 Mcgraw Hill Higher Education




Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download




Solved Many Seed Plants Can Reproduce Sexually Or Asexual Chegg Com




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica




Plants Without Seeds Plant Reproduction Dk Find Out



1




Angiosperms Features Classification Reproduction Videos Examples




Plant Propagation Wikipedia




Exploring Plant Reproduction And Seed Dispersal Grade 9 Petal Flowers
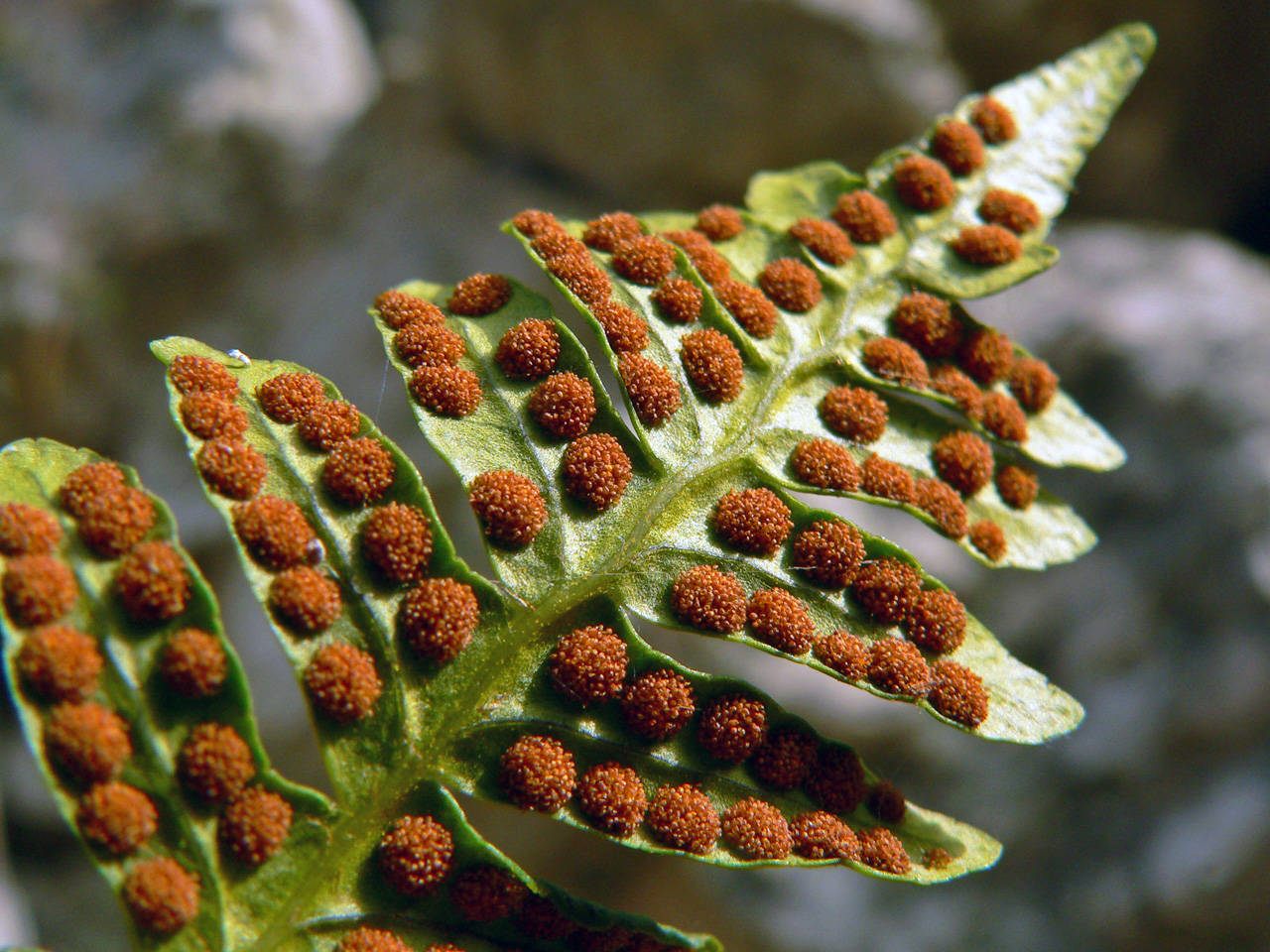




Fifth Grade Plant Reproduction Non Seed Plants



No comments:
Post a Comment